Tooltip
Tooltips add additional context to interactive UI elements and appear on mouse hover or keyboard focus.
On this page
On this page
Usage
- Reserve tooltips to visually surface the label for icon buttons.
- Keep the tooltip text minimal.
- Never include tooltips on non-interactive components (
div,span,p) because it will not be accessible for keyboard or screen reader users.
Best practices
Use a tooltip on an icon button to help convey the purpose of the action
Don't use tooltips on non-interactive elements
Options
Label
Icon buttons have a visually hidden label utilizing `aria-label`. To instead display that label in a tooltip, the `label` option should be used. The `label` serves as the accessible name for the control utilitizing `aria-labelledby` under the hood.
Description
The description is intended to supplement the control's text label by utilitizing aria-describedby under the hood, and will be announced to a screen reader in addition to the label. Keep the description short and concise.
Icon button with visually hidden label
Icon buttons have a visually hidden label utilizing `aria-label`. To provide context in addition to the visually hidden label, use the `description` option.
Button with visible label
For buttons that have a visible label, the `description` option can also be used to provide additional context.
Position
By default, the Tooltip component will position itself below the interactive control in a centered alignment. The position is dependant on the space available within the viewport, and it will never break outside of it. It may appear to the top, bottom, left, or right of the interactive control.
Alternatives to tooltips
Before adding a tooltip, please consider: Is this information essential and necessary? Can the UI be made clearer? Can the information be shown on the page by default? See Tooltip alternatives for more accessible alternatives.
We use aria-label for tooltip contents. However, aria-label replaces the text content of an element in screen readers, so only use Tooltip on elements with no existing text content.
A tooltip may only be used on an element that is interactive such as a button or a link. Even if an element is focusable, a tooltip may only be used if the element does something when it's clicked.
1. Persist the content
If possible, persist the content so it's always available rather than using a tooltip, which hides content by default. This ensures that the content is always discovered and surfaced to users regardless of device.
Find an appropriate permanent place to display additional information.
Don't use a tooltip to add additional helpful information
2. Don't duplicate content
If the tooltip duplicates content that is already available on the page, remove it.
Remove any duplicate tooltip text.
Don't set tooltips that duplicate the trigger element content.
3. Use a modal
Consider using a modal, which is accessible for mobile users and allows you to structure content that may otherwise be crammed into a tooltip.
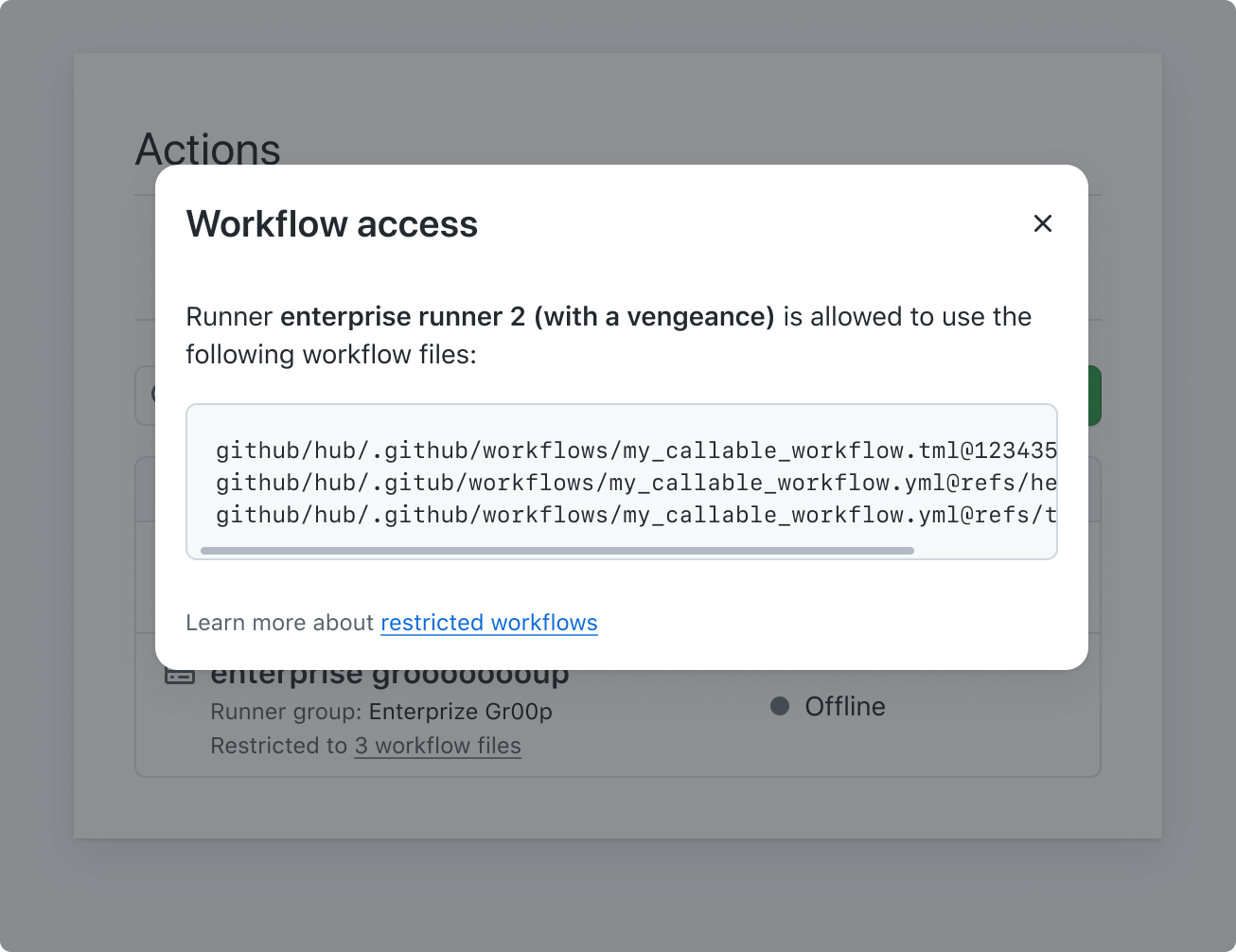
Do use a pattern that is accessible to a larger number of users such as a modal
Don't place long content inside a tooltip
4. Use a summary disclosure
Consider using a summary disclosure that is accessible for mobile users and also offers the ability to show or hide content.
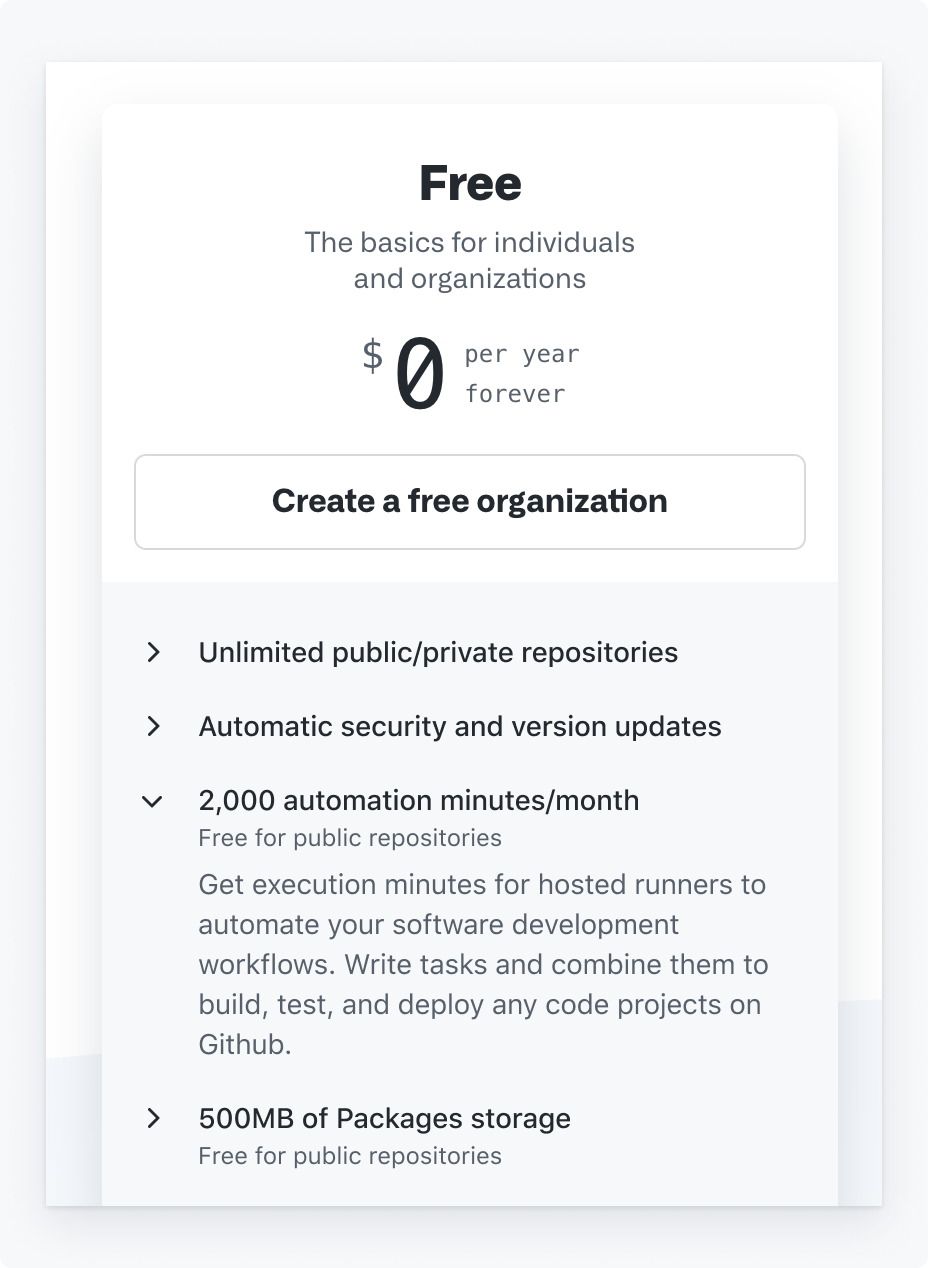
Do use a pattern that is accessible to a larger number of users such as a summary disclosure
Don't use tooltips on non-interactive elements
Other
If you are unsure which alternative is more suited to your scenario and need help, consult a designer or the GitHub Accessibility team (if you are GitHub staff) for advice.